Are you curious about how your car’s air conditioning (A/C) system works? Understanding the A/C diagram and its components can help you troubleshoot problems, properly maintain the system, and ensure optimal cooling performance. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of an A/C diagram in a car, explain its key components, discuss its functioning, and provide essential maintenance tips.
What is an A/C Diagram in a Car?
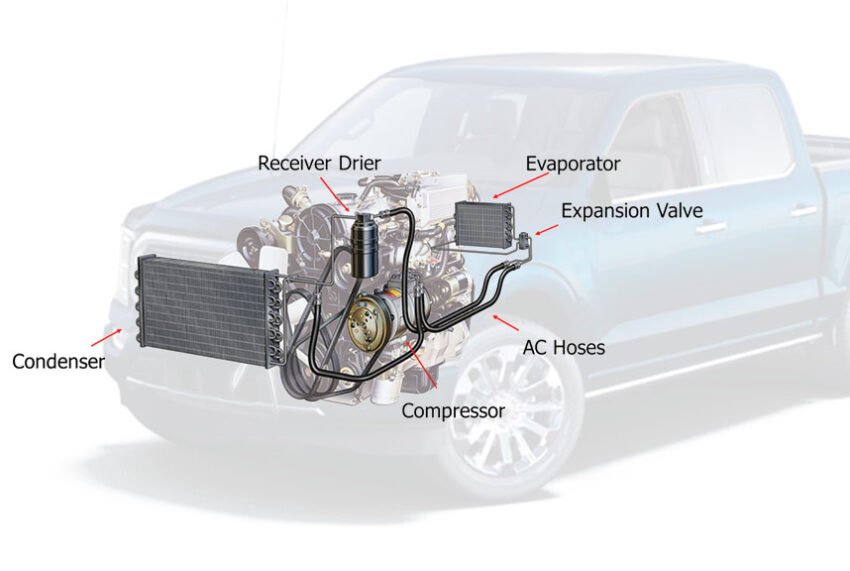
An A/C diagram, also known as an air conditioning schematic, illustrates the configuration and layout of the air conditioning system in a vehicle. It provides a visual representation of the system’s components and their interconnections. By referring to the A/C diagram, mechanics and car owners can understand the overall design and how different parts work together to achieve efficient cooling.
One important component of the A/C system is the fan clutch. The fan clutch controls the cooling fan’s speed, which helps regulate the engine’s temperature. In normal conditions, the fan clutch engages and disengages according to the engine’s cooling needs. However, if the fan clutch stuck engaged, it means that the fan is continuously spinning at full speed, even when it’s not required. This can lead to unnecessary noise, increased fuel consumption, and decreased engine performance.
Components of an A/C Diagram
Let’s take a closer look at the primary components found in an A/C diagram:
- Compressor: The compressor is a vital component that pressurizes the refrigerant, transforming it from a low-pressure gas into a high-pressure gas.
- Condenser: The condenser helps dissipate heat from the refrigerant, causing it to liquefy and release the absorbed heat into the surrounding air.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of the refrigerant, converting it from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure mist before it enters the evaporator.
- Evaporator: The evaporator cools the warm air from the cabin by absorbing heat. As the refrigerant evaporates, it reduces the temperature of the air blown into the vehicle.
- Refrigerant: The refrigerant is a specialized fluid that cycles through the A/C system, absorbing heat from the cabin and releasing it outside the vehicle.
How Does an A/C Diagram Work?
To understand how the A/C diagram functions, it’s essential to comprehend the basic working principles of an air conditioning system in a car. The A/C system operates in a continuous cycle, utilizing the compression and expansion of the refrigerant to cool the air inside the vehicle.
When the A/C system is activated, the compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure gas. This gas then flows into the condenser, releasing heat and condensing into a high-pressure liquid. The high-pressure liquid passes through the expansion valve, reducing its pressure and transforming it into a low-pressure mist. As the refrigerant enters the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, resulting in a significant temperature drop. Finally, the cool air is blown into the cabin, providing a comfortable environment.
Understanding the A/C Circuit
The A/C circuit encompasses both electrical connections and refrigerant flow. Proper functioning of both aspects is crucial for efficiently operating the A/C system.
Regarding electrical connections, the A/C system relies on various sensors, switches, and relays to control the compressor, fans, and other components. These electrical elements ensure the system operates at the desired settings and protects it from potential damage.
Regarding refrigerant flow, the A/C system utilizes a closed-loop circuit. The refrigerant circulates through the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator, absorbing and releasing heat. This continuous cycle enables the A/C system to maintain a cool and comfortable cabin temperature.
Common Issues with A/C Systems
While A/C systems are designed to provide reliable cooling, they can encounter certain problems over time. Here are some common issues you may face:
- Insufficient Cooling: If your A/C system is not cooling adequately, it could be due to low refrigerant levels, a malfunctioning compressor, or a clogged condenser.
- Strange Noises: Unusual noises, such as squealing or rattling, may indicate a problem with the A/C system, such as a worn-out compressor clutch or a loose belt.
- Leaks: Refrigerant leaks can lead to a gradual loss of cooling performance. Identifying and repairing these leaks is crucial for restoring the system’s efficiency.
- Foul Odors: A/C systems can develop unpleasant odors due to mold or mildew growth within the evaporator or ductwork. Regular maintenance can prevent such issues.
To address these issues, it’s essential to troubleshoot and diagnose the problem accurately.
Troubleshooting A/C Problems
When troubleshooting A/C problems, consider the following steps:
- Checking the Refrigerant Levels: Insufficient refrigerant can result in reduced cooling capacity. Use a pressure gauge to determine if the refrigerant levels are within the recommended range.
- Examining the Compressor: Inspect the compressor for any signs of damage or leaks. A faulty compressor may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Inspecting the Condenser: Ensure the condenser is clean and debris-free. A clogged condenser can hinder the dissipation of heat and compromise cooling efficiency.
- Cleaning the Evaporator: Regularly clean the evaporator to prevent the buildup of mold or dirt, which can impede its cooling performance.
Maintaining and Servicing the A/C System
To keep your car’s A/C system in optimal condition, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Have your A/C system inspected by a qualified technician at least once a year to detect potential issues early on.
- Cleaning the Filters: Clean or replace the air filters regularly to ensure proper airflow and prevent the accumulation of dust and debris.
- Recharging the Refrigerant: If your A/C system is low on refrigerant, consult a professional to recharge it properly. Adding refrigerant without considering the recommended levels can lead to performance problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the A/C diagram and the key components of your car’s cooling system empowers you to troubleshoot problems and maintain the system effectively. Regular inspections, proper cleaning, and timely repairs can enhance the longevity and performance of your A/C system. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a comfortable and refreshing driving experience.
You may like to read How to Solve Dishwasher Leaking from the Front

