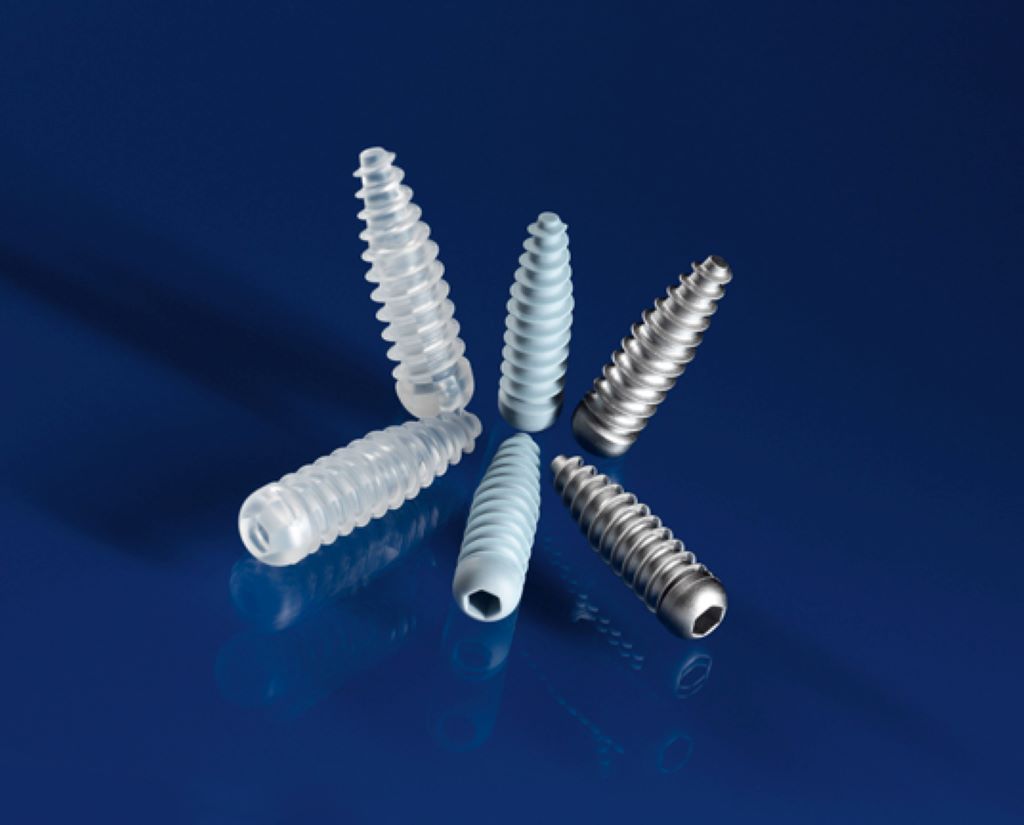
Surgical screws are typically made of stainless steel, titanium, or biocompatible materials. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body. Stainless steel screws are commonly used due to their affordability and resistance to corrosion. Titanium screws are often used for their lightweight properties and high biocompatibility. Biocompatible materials, such as bioabsorbable screws, are designed to gradually dissolve in the body over time.
This allows for natural healing without the need for a second surgery to remove the screws. The choice of material depends on factors such as the location of the surgery, the specific needs of the patient, and the surgeon’s preference.
The Basics Of Surgical Screws
Surgical screws, as detailed on Heartandstylewoman.com, are commonly used in orthopedic surgeries to hold bones together during the healing process. They play a crucial role in stabilizing fractures and ensuring proper alignment. These tiny screws are made of various materials and designed with different specifications to meet the unique requirements of each surgical procedure. Their precise design and material choice are essential for the success of the surgical outcome, contributing significantly to the patient’s recovery and the overall effectiveness of the orthopedic treatment.
Materials Used
Surgical screws are manufactured using a range of biocompatible materials to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and promote successful healing. The choice of material depends on factors such as the patient’s medical condition, the location of the surgery, and the surgeon’s preference. The most commonly used materials for manufacturing surgical screws include:
- Titanium: Known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, titanium is a popular choice in surgical screw production. Its biocompatibility allows for bone integration, while its lightweight nature ensures minimal stress on the surrounding tissue.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is widely used due to its high tensile strength and affordability. It provides excellent stability and durability, making it suitable for various orthopedic procedures.
- Co-cr Alloy: A combination of cobalt and chromium, Co-cr alloy possesses excellent wear resistance and biocompatibility. It is commonly used in load-bearing applications, such as spinal fusion surgeries.
- Biodegradable materials: In some cases, biodegradable materials like PLA (polylactic acid) or PLLA (poly L-lactic acid) may be used, especially in pediatric cases. These materials gradually dissolve over time, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the screws.
Screw Design
Screw design plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and stability of surgical implants. The structure and features of the screws vary based on the surgical application. Some common screw designs include:
- Cortical Screw: This type of screw has a partially threaded shaft and is primarily used in dense bone regions like the femur or tibia.
- Cancellous Screw: Cancellous screws have a fully threaded shaft and are specifically designed for softer bone structures such as the vertebrae.
- Locking Screw: Locking screws are used in conjunction with specialized plates to provide enhanced stability. They have a threaded portion near the head that locks into the plate, preventing movement.
Surgeons need to select the appropriate screw design based on the patient’s specific anatomy and the surgical objective to ensure successful outcomes.
The Importance Of Material Selection
Surgical screws are typically made of strong and biocompatible materials such as titanium or stainless steel. The choice of material is crucial as it directly impacts the implant’s strength and compatibility with the patient’s body, ensuring successful surgical outcomes. Careful material selection is essential to prevent complications and promote effective healing. Additionally, for patients who have undergone surgeries involving these screws, knowing how to tell if surgical screws are loose is vital for monitoring their condition and ensuring timely medical intervention if needed. This awareness can significantly contribute to the long-term success of the surgical procedure.
The Importance of Material Selection When it comes to surgical screws, the selection of the material plays a crucial role in determining the success of the surgery. The material used must possess certain characteristics to ensure the optimal performance of the screws. In this section, we will explore the importance of material selection by examining two key factors: biocompatibility and the strength and durability of the screws.
Biocompatibility: Biocompatibility refers to the ability of a material to coexist with living tissue without causing any harm or adverse reactions. In the case of surgical screws, the material must be biocompatible as they are directly implanted into the body. The material should not elicit an immune response, allergic reactions, or toxicity. Choosing a biocompatible material ensures that the patient’s body accepts the screws without any complications. Materials commonly used for surgical screws include titanium and stainless steel. These materials are known for their excellent biocompatibility, making them suitable choices for various surgical procedures.
Strength and Durability: In addition to biocompatibility, the strength and durability of surgical screws are equally important factors to consider during material selection. Surgical screws need to withstand the forces and stresses placed on them after implantation. They must provide stability and support to the bone, promoting faster healing and minimizing the risk of complications. Materials with high strength and durability, such as titanium alloys, are preferred for surgical screws. These materials exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including tensile strength and fatigue resistance, ensuring the screws can withstand the demands of the body and the surgical procedure itself.
Additionally, such materials are less prone to corrosion, maintaining their functionality over time. In conclusion, when it comes to surgical screws, selecting the right material is of utmost importance. The material must possess both biocompatibility and the necessary strength and durability for successful implantation. By choosing materials such as titanium and stainless steel, surgeons can ensure that the screws function optimally, supporting the healing process and promoting positive patient outcomes.
Types Of Surgical Screws
Surgical screws are crucial medical devices used in orthopedic and other surgical procedures to stabilize bone fragments and implants. The choice of material for surgical screws depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition and the surgical site. The two most commonly used materials for surgical screws are titanium and stainless steel.
Titanium Screws
Titanium screws are highly favored in surgical procedures due to their biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and low density. These screws are often used in orthopedic and craniofacial surgeries, as they’re lightweight and offer excellent strength. Furthermore, titanium screws also allow for better visualization of X-rays, making postoperative assessments easier.
Stainless Steel Screws
Stainless steel screws are another popular choice, known for their exceptional strength and durability. They are commonly used in orthopedic and trauma surgeries, as they provide reliable fixation for bone fractures and implants. While stainless steel screws may be less biocompatible compared to titanium, they are still widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and proven track record in medical applications.
Innovations In Surgical Screws
Surgical screws have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery, providing stability and support to fractured bones. Over the years, advancements in medical technology have led to the development of innovative surgical screws with improved functionalities. In this article, we will explore two cutting-edge innovations in surgical screws: Bioabsorbable Screws and Smart Screws.
Bioabsorbable Screws
Bioabsorbable screws are a remarkable innovation in orthopedic surgery. As the name suggests, these screws are designed to be gradually absorbed by the body, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove them. Made from biocompatible materials such as polylactic acid (PLA) or polyglycolic acid (PGA), these screws provide temporary fixation during the healing process.
One of the key advantages of bioabsorbable screws is that they reduce the risk of implant-related complications, such as loosening or migration. Traditional metallic screws may sometimes irritate the surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort and long-term complications. Bioabsorbable screws, on the other hand, minimize the chances of such issues, allowing for a smoother healing process.
Furthermore, bioabsorbable screws provide gradual load sharing with the surrounding bone, promoting natural healing and minimizing stress shielding. This is particularly beneficial in cases where the bone is still growing or in pediatric orthopedic surgery. The gradual degradation of the screw also allows for optimal bone remodeling, resulting in a stronger and more natural bone structure.
It is important to note that bioabsorbable screws are not suitable for all procedures and patients. Factors such as the location and type of fracture, bone density, and patient’s age must be carefully considered before opting for this innovative solution. Consultation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Smart Screws
Another groundbreaking advancement in surgical screws is the development of smart screws. These screws are equipped with advanced sensors and microchips, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis during and after surgery. By incorporating smart technology, surgeons and healthcare professionals can obtain valuable insights about the healing process, implant performance, and patient outcomes.
The sensors embedded within smart screws can measure various parameters such as strain, load, temperature, and pressure. This data can be wirelessly transmitted to a monitoring device, enabling continuous and remote monitoring of the implant and the patient’s progress. The ability to monitor and analyze real-time data can help identify potential complications early on and make informed decisions regarding the course of treatment.
Smart screws have the potential to revolutionize postoperative care and patient management. By providing objective measurements and insights, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans based on individual patient needs, ensuring optimal recovery and long-term outcomes. Additionally, the data collected from smart screws can contribute to advancements in orthopedic research and the development of new treatment protocols.
While the use of smart screws is still in its early stages, the potential applications and benefits are promising. However, like any new technology, thorough research and clinical studies are essential to validate their efficacy and safety. As the field of orthopedics continues to evolve, innovative solutions like smart screws have the potential to further enhance patient care and outcomes.
Future Trends In Surgical Screw Technology
The field of surgical screw technology is constantly evolving, paving the way for promising future trends. With advancements in nanotechnology applications and enhanced imaging integration, surgical screws are becoming more efficient and effective than ever before.
Nanotechnology Applications
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing the medical industry, and surgical screws are no exception. By utilizing materials at the nanoscale level, these tiny screws can be enhanced to provide improved strength and biocompatibility. Researchers are exploring novel nanomaterials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and nanocrystalline metals, which offer superior mechanical properties and accelerate the healing process.
The use of nanocoatings on traditional surgical screw materials, such as titanium, also allows for enhanced osseointegration, preventing complications like loosening or dislodgement. This innovative technique provides a secure anchor within the bone, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of surgical revision.
Enhanced Imaging Integration
To optimize surgical outcomes, integrating advanced imaging technologies with surgical screw placement has become increasingly important. Surgeons can now utilize tools like intraoperative CT scans, MRI, and real-time fluoroscopy to guide screw insertion more accurately than ever before. These imaging techniques empower surgeons to precisely assess bone density and identify potential complications, ensuring screws are placed in the optimal position.
Additionally, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems are being developed to assist surgeons in visualizing screw placement in real time. With the help of AR or VR headset, surgeons can visualize and navigate the surgical site, leading to improved accuracy and reducing the risks associated with extensive exploratory procedures.
The future trends in surgical screw technology hold great promise for enhancing patient outcomes and improving surgical procedures. Nanotechnology applications and enhanced imaging integration are just two areas that show immense potential. As research and development in these fields continue, we can expect surgical screws to become even more precise, durable, and successful in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Are Surgical Screws Made Of
What Are Surgical Screws Made Of?
Surgical screws are typically made of implant-grade materials such as titanium or stainless steel. These metals are chosen for their strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body. Titanium screws are often preferred due to their lighter weight and lower risk of allergic reactions.
Stainless steel screws are also widely used for their corrosion resistance and high strength.
Conclusion
Surgical screws are commonly made of titanium or stainless steel, ensuring durability and compatibility. Understanding the materials used in surgical screws is essential for both medical professionals and patients. Cavitation, a process utilized by ultrasonic cleaning devices and certain surgical instruments to break down tissue or debris, plays a critical role in modern medical procedures. This knowledge allows for informed decisions and successful surgical outcomes. With advancements in technology, the use of biocompatible materials continues to improve patient care and recovery.